Valence Electrons
The electrons in the outermost orbit of an atom are known as valence electrons.
The outermost orbit can have a maximum of 8 electrons i.e. the maximum number of valence electrons can be 8. The valence electrons determine the physical and chemical properties of a material. These electrons determine whether or not the material is chemically active; metal or non-metal or, a gas or solid. These electrons also determine the electrical properties of a material.
On the basis of electrical conductivity, materials are generally classified into conductors, insulators and semiconductors. As a rough rule, one can determine the electrical behaviour of a material from the number of valence electrons as under:
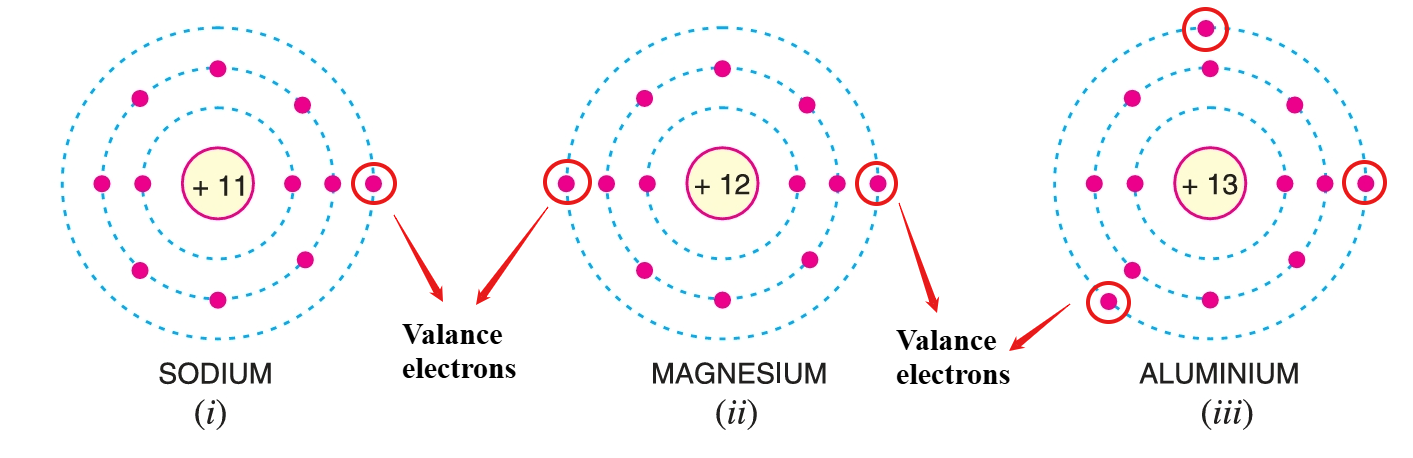
- When the number of valence electrons of an atom is less than 4 (i.e. half of the maximum eight electrons), the material is usually a metal and a conductor. Examples are sodium, magnesium and aluminium which have 1, 2 and 3 valence electrons respectively.
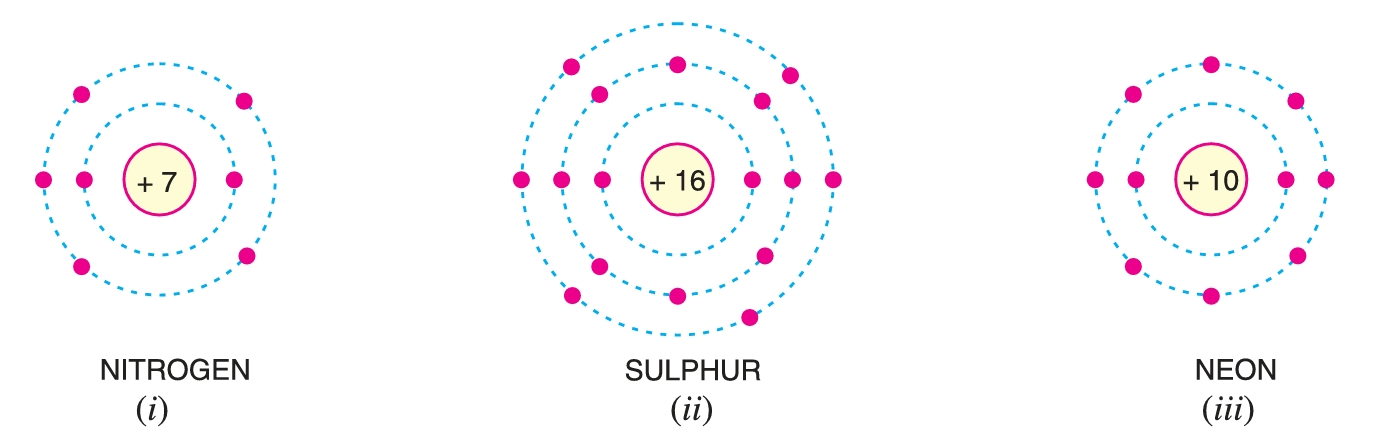
- When the number of valence electrons of an atom is more than 4, the material is usually a non-metal and an insulator. Examples are nitrogen, sulphur and neon which have 5, 6 and 8 valence electrons respectively
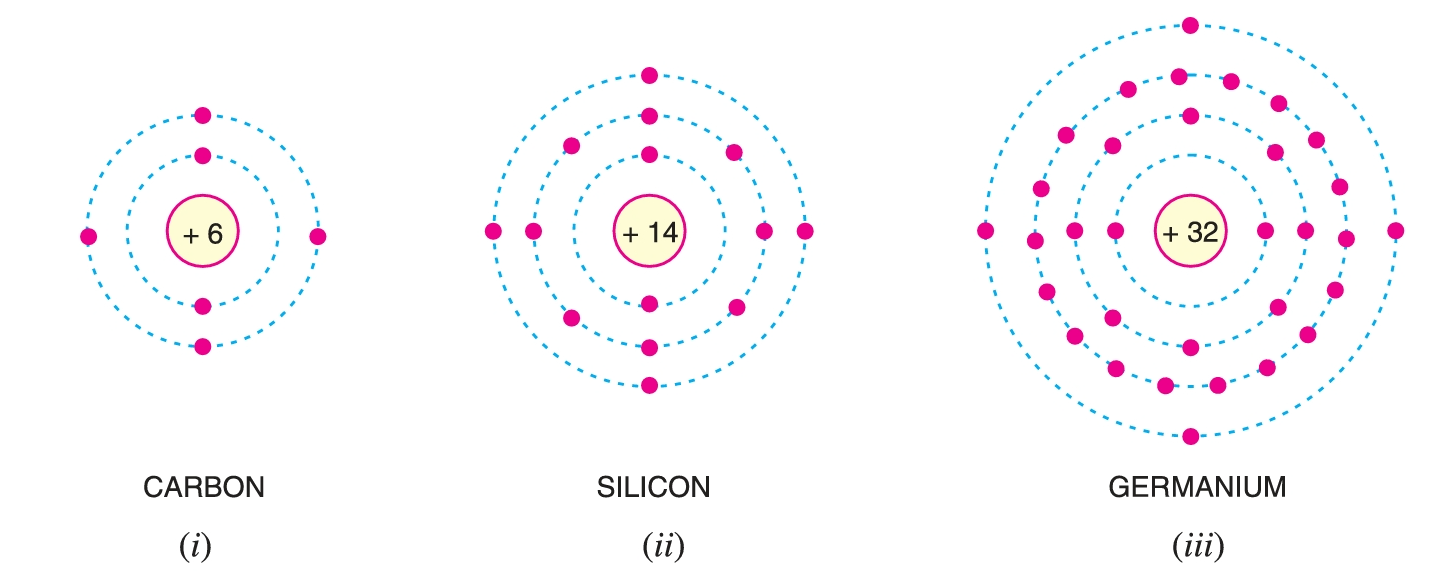
- When the number of valence electrons of an atom is 4 (i.e. exactly one-half of the maximum 8 electrons), the material has both metal and non-metal properties and is usually a semiconductor. Examples are carbon, silicon and germanium.